Word has it that Juncker is socially conservative and therefore does not relish the migrant crisis; but he is a businessman who is looking after business interests for himself, business constituents and to maintain his position as an EU representative of those interests.

That is why he felt constrained to put across a plan to try to preserve the Schengen zone by diffusing responsibility among its members and (in his theory) that might dilute the impact of the migrants.
An additional aspect to the psychology of his position is that he is from Luxembourg, one of the smallest European nations. One can imagine business persons from small countries finding the delay and tedium of having to go through border controls as they move in and out of a Luxembourg every 15 minutes an insufferable handicap.
Nevertheless, from a WN/ethnonationalist perspective, particularly until such time as the borders of the entire zone are secure from non-European imposition and those who are already here are drastically reduced in number by means of repatriation, the Schengen zone will have to give way to tighter national border controls.
From an ethnonationalist point of view, in any event, there has to be more national accountability to their own and to European people as a whole.
Is this the end of Schengen?

Sep 16 2015: In last week’s State of the Union speech, European Commission President Jean-Claude Junker referred to the Schengen Area – a border-free travel zone made up of 26 European countries – as “a unique symbol of European integration”. After Germany’s recent announcement that it would be “temporarily reintroducing border controls”, some say that unique symbol is in jeopardy.
A look back at the past 30 years since the agreement was signed can help clarify what exactly is at risk.
What is Schengen?
The Schengen Area is made up of 26 European countries that have removed border controls at their shared crossings. The agreement was signed in 1985 by five members of the EU, and came into force 10 years later. Following the 1997 Amsterdam Treaty, the Schengen agreement became part of European law. That meant all new EU members had to sign up to it, although Britain and Ireland had already been given the right to opt out. As the map below shows, four non-EU countries – Switzerland, Iceland, Norway and Liechtenstein – are also members of the area.
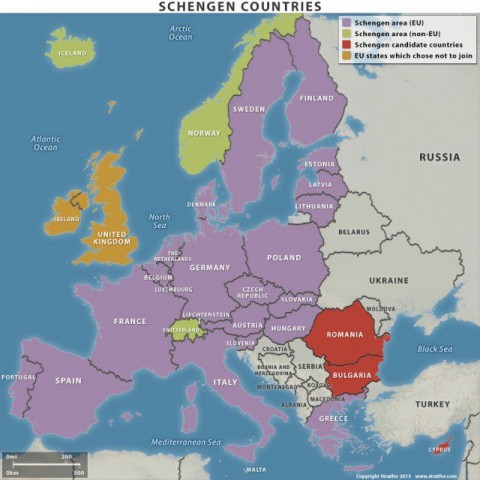
Why are people talking about the end of Schengen?
We are experiencing a global refugee crisis. Around the world, 60 million people have been forced to flee war, violence and human rights abuse – levels not seen since World War II. Hundreds and thousands of those people have attempted the often perilous journey to Europe in search of a better, safer life.
Some of them haven’t made it – while the image of Aylan Kurdi’s lifeless body on a beach in Turkey shocked the world, many more have died trying to get to Europe. According to figures from the International Organization for Migration, 2015 could end up being the deadliest on record.
Of those who do make it over, the majority have been heading to Germany. The country expects to take in 1 million asylum seekers by the end of the year, more than all other EU countries collectively received in 2014. It is in response to these huge numbers that Germany decided to re-impose its internal border controls. The country’s interior minister said the move aimed to “limit the current inflows to Germany and to return to orderly procedures when people enter the country”.
Some have been quick to emphasize the temporary nature of this decision. But with countries such as Austria and the Netherlands now following suit, others think Schengen’s days are numbered.
Has anything like this happened before?
The option for a country to temporarily reinstate border controls was actually built into the original agreement, as the European Commission pointed out last weekend: “The temporary reintroduction of border controls between member states is an exceptional possibility explicitly foreseen in and regulated by the Schengen Borders Code.”
In the past, countries have chosen to exercise that right. For example, in 2006 Germany reinstated border controls when it hosted the FIFA World Cup. France did the same in 2005, following the terrorist attacks in London. In what was perhaps a precursor of the troubles to come, during the post-Arab Spring mass migration of 2011, politicians in France and Italy called for deep reforms to the agreement.
So what’s different this time?
Even in Schengen’s early days, critics pointed to one big flaw: freedom of movement within the Schengen area only works if the common external borders are fortified. With many frontline countries such as Greece already experiencing crises of their own, the task of strengthening those external borders has become even tougher.
The stakes were raised this summer after a heavily armed terrorist suspect was apprehended on board a train travelling between three Schengen countries. The ease with which he had moved around the area prompted some to refer to Europe’s open-border policy as a terrorist’s paradise.
Perhaps more importantly, people’s attitudes within the area are starting to change. This recent crisis is just one in a long line of turbulent events for Europe these past months and years. Whether they are right to do so, some blame the union for these developments. While Schengen and the free movement of people might be at the core of the European project, for some that no longer seems worth fighting for. A poll back in July showed that the majority of western Europeans would like to see Schengen scrapped, and last year former French President Nicolas Sarkozy called for it to be “immediately suspended”.
But with so many people now displaced by conflict and violence, others argue that the European project – which has brought peace to a continent previously locked in war – has never been more important.
As plans to share out asylum seekers more equitably across the European Union make little progress, many will be closely watching the developments for hints of what it means for Schengen.
